Style Sampler
Layout Style
Melanoma
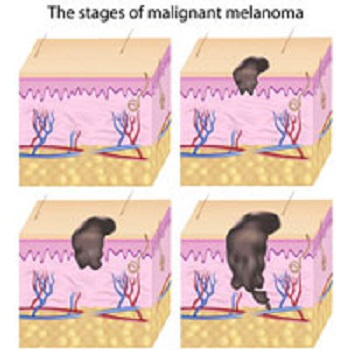
Cancer that develops from skin melanocytes is called melanoma (other names: skin melanoma, malignant melanoma)
Frequency-Causes
Ultraviolet ( UV ) radiation from the sun is the usual risk factor.
People with red or blond hair, blue eyes and generally light skin are more prone to melanoma.
The risk is also higher in people with dysplastic nevi, with a history of severe sunburn in childhood and a family history of melanoma. There is an increase in frequency in the modern western world due to exposure to ultraviolet radiation, especially in places where the ozone hole makes the sun even more dangerous. Of particular importance is the sudden and prolonged exposure to the sun.
Symptoms – Diagnosis
Often, the first sign of melanoma is a change in the size, shape or color of an a skin mole. Normally a nevus is a brown, dark or black mark on the skin. It can be flat and the shape can be round or oval. The nevi are usually small, less than 0.5 cm. Most people have 10-30 moles on their skin. The vast majority of them are completely harmless. Nevertheless, all nevi should be mapped. However, a change in a nevus (eg asymmetry, irregular borders, discoloration, increase in diameter, itching, bleeding) means that you should see your dermatologist. It is important to know that melanoma can also appear as a new nevus.
Melanoma in men occurs more often in the trunk, head and neck. In women, it usually occurs on the arms and legs. It can also occur in the eye or anus.
The biopsy will make the final diagnosis. It is recommended to remove the entire nevus for biopsy. Of great importance is the depth of infiltration calculated on the basis of the Breslow scale as well as the evaluation of the sentinel lymph node. Early diagnosis is crucial for the prevention of metastases.
Treatment
Most patients are treated surgically. In patients with melanoma, the local extent of the disease largely determines the risk of recurrence or metastasis. Lymph node infiltration increases the risk of recurrence to 86%. In the more advanced stages, adjuvant therapy is recommended.
The potential for chemotherapy is limited compared to other diseases, but the use of immunotherapy and other targeted therapies (such as BRAF inhibitors ) has excellent results in both early disease and metastasis.